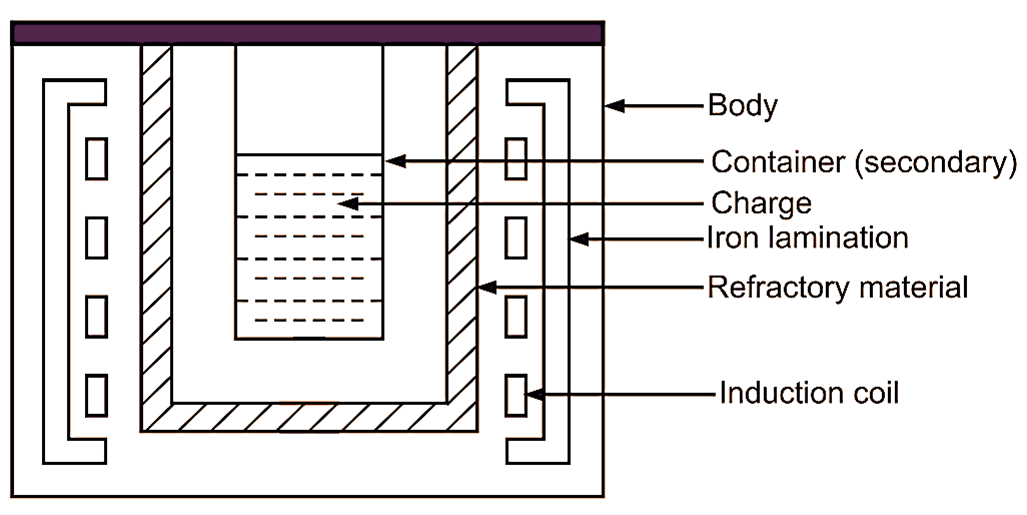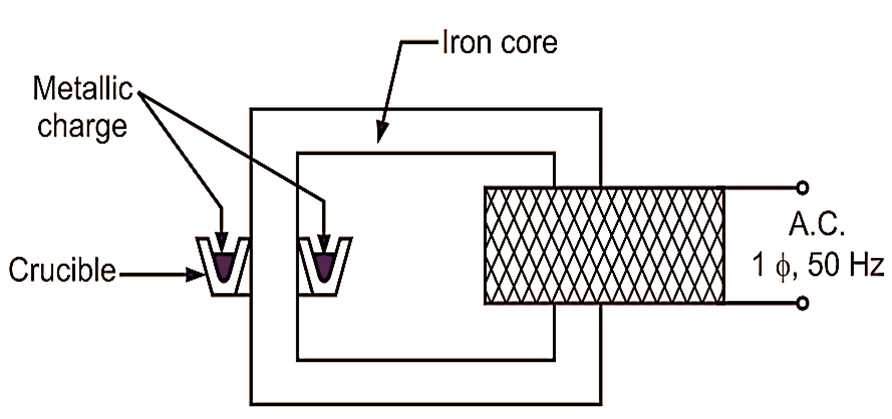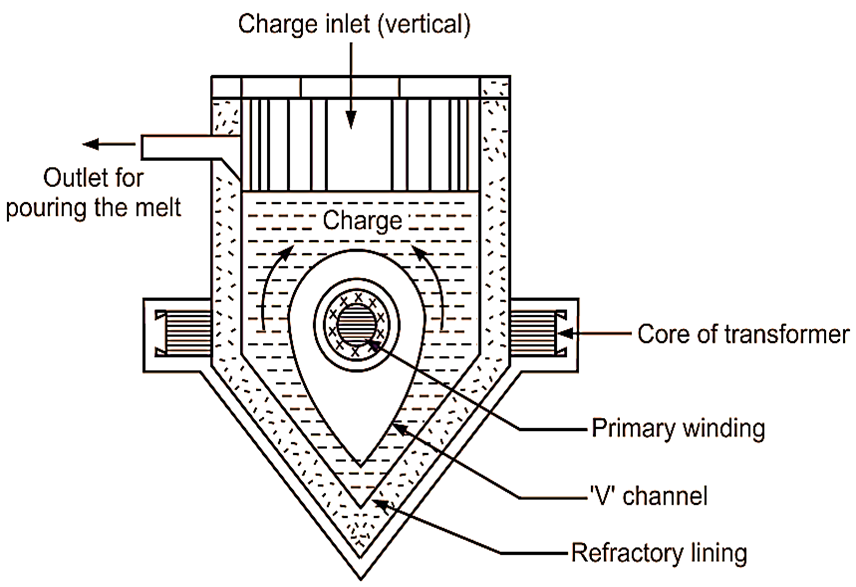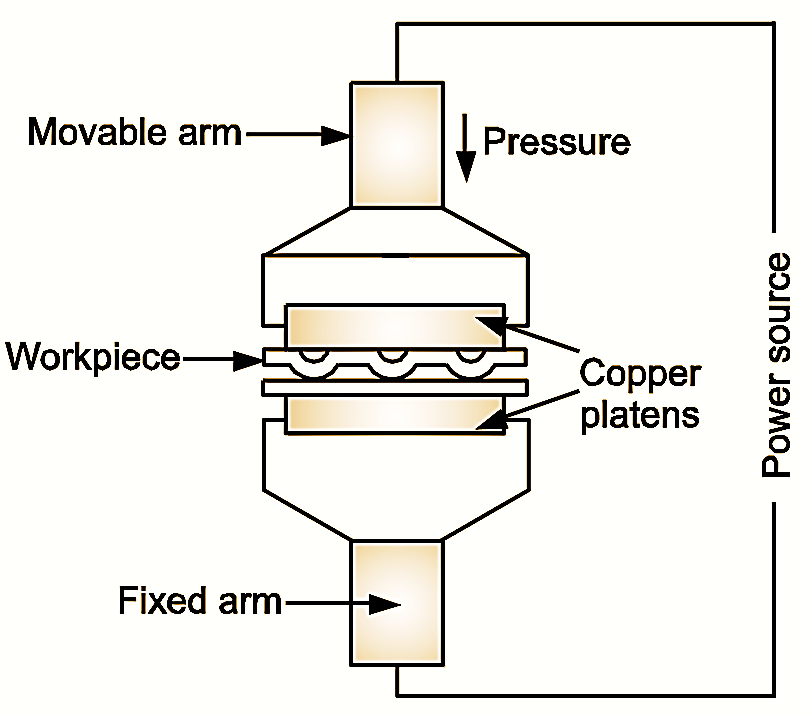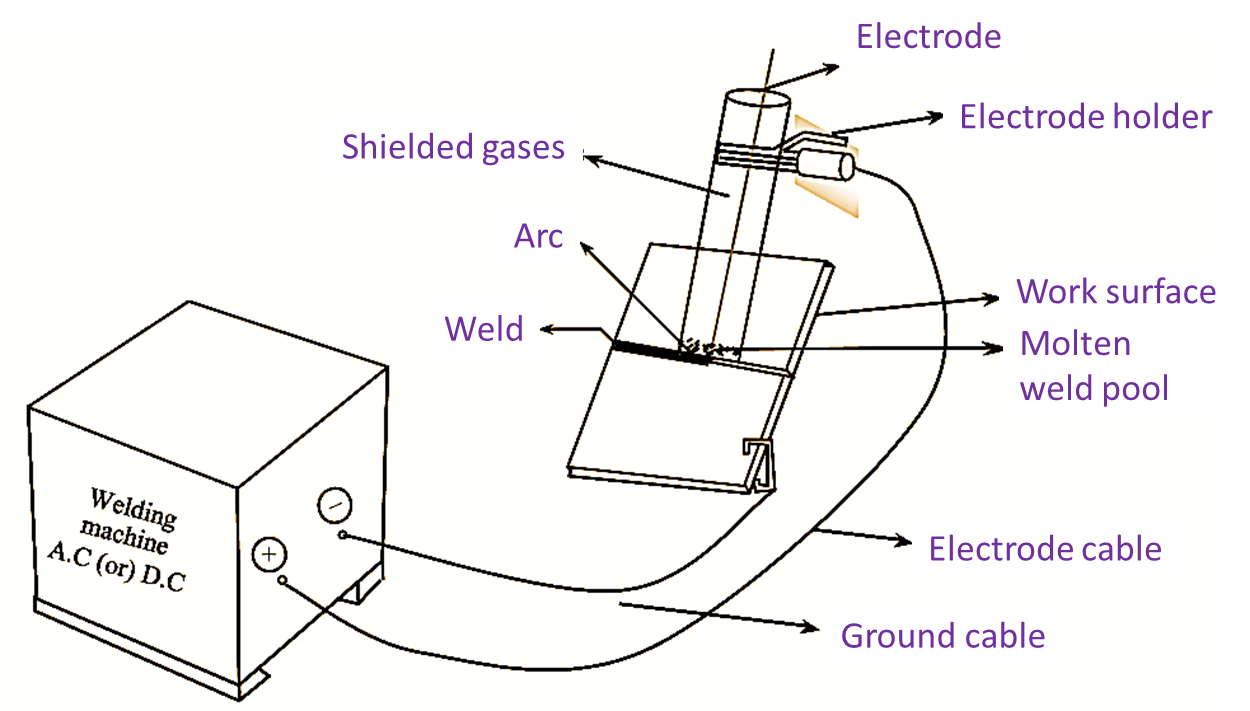
Figure 1: Shielded Metal Arc Welding.
The manual metal arc welding is also known as shielded metal arc welding or metal arc welding process. It is an arc welding process, wherein the welding is done by heating the workpiece with an electric arc set up between a flux coated electrode and the workpiece. Continue reading What is Shielded Metal Arc Welding? Process, Diagram, Advantages & Applications