The Light Activated Silicon Controlled Rectifier (LASCR) is abbreviated as LASCR. It is a very popular control element in the photoelectric thyristor family. It can be triggered by optical radiation. Its trigger sensitivity is maximum for a light of wavelength 0.8 to 1.5 μm. The device of 6000 V and 1500 A is commercially available. It is also called photo SCR. LASCR is a semiconductor optoelectronic switch having higher power handling capacity than that of other semiconductor optoelectronic devices. It uses small amount of light energy to control much larger amount of electrical energy.
Construction of Light-Activated SCR
The construction of a LASCR is similar to SCR in its layout, but it has a light sensitive gate. Fig. 1 (a) shows the constructional details of a LASCR. As LASCR is a light sensitive device, it is provided with a glass top to enter the light. To achieve the sensitivity of the device to the light, a thin silicon pellet of small dimensions is provided in it. The gate structure is designed to provide sufficient gate sensitivity for triggering from practical light sources such as LEDs. The high sensitivity of LASCR also causes it to respond to other effects such as temperature, applied voltage and rate of change of applied voltage.
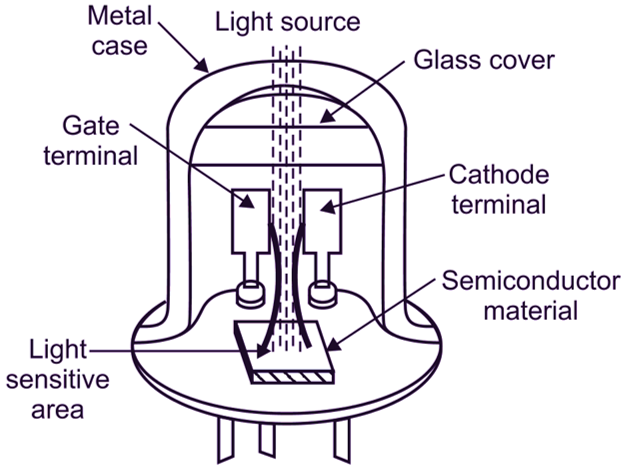
(a) Constructional details
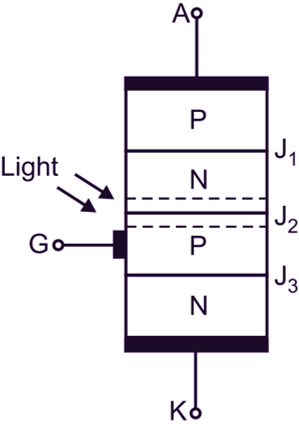
(b) Structure
(c) Symbol
Fig. 1: Construction of LASCR
The basic structure of a LASCR is as shown in Fig. 1 (b). The LASCR has a similar constructional structure as SCR, i.e. PNPN device. As the LASCR is photosensitive, it is provided with a glass top to enter the light input. It is also provided with a lens at the top to focus the light on the gate. It has three terminals such as anode, cathode and gate. It can be turned ON by direct radiation on the silicon wafer of gate with light. It has a longer turn-OFF time as compared to normal SCR. The symbol of a LASCR is as shown in Fig. 1 (c).
Principle of Operation of Light Activated SCR
The structure of a LASCR with proper biasing is as shown in Fig. 2. The LASCR is forward biased by a supply voltage VS. For maximum sensitivity, the gate G is left open.
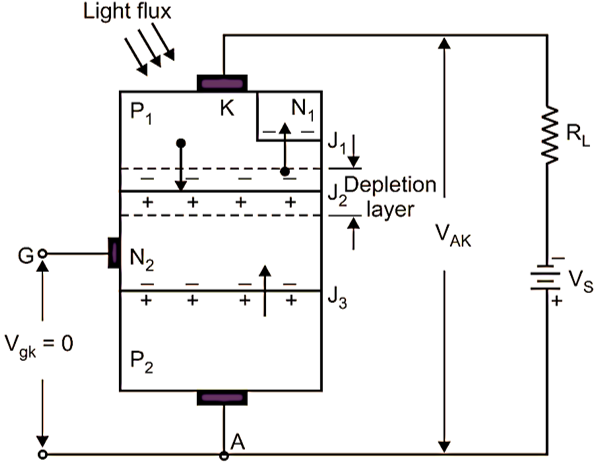
Fig. 2: Operation of LASCR
When the light is not incident through the transparent window on the P1 base layer, the LASCR does not conduct the current because the junction J2 is reverse biased. Thus in the absence of light, the LASCR is OFF. This is a forward blocking (OFF) state of the LASCR. When the light is incident through the transparent window on the P1 base layer, it will create the number of electron-hole pairs in this P1 layer, if the intensity of light is strong. These electron-hole pairs diffuse towards the junctions J1 and J2. On entering the carriers in the depletion layer, its width reduces and also reduces the reverse biasing across the junction. The injected carriers in the junction J2 reduce the reverse biases and further reduce the depletion layer so that the breakdown of junction J2 takes place and the current flows through the LASCR from anode to cathode. Thus in the presence of light, the LASCR turns ON. This is a forward conduction (ON) state of a LASCR. The LASCR can be turned ON with a positive pulse voltage at the gate G by incidenting the light. This has a low sensitivity of light. A variable resistor Rp may be connected between gate and cathode to change the sensitivity of the circuit to the light intensity.
V-l Characteristics of Light Activated SCR
The V-l characteristics of a LASCR is as shown in Fig. 3. The LASCR is forward biased with open gate.
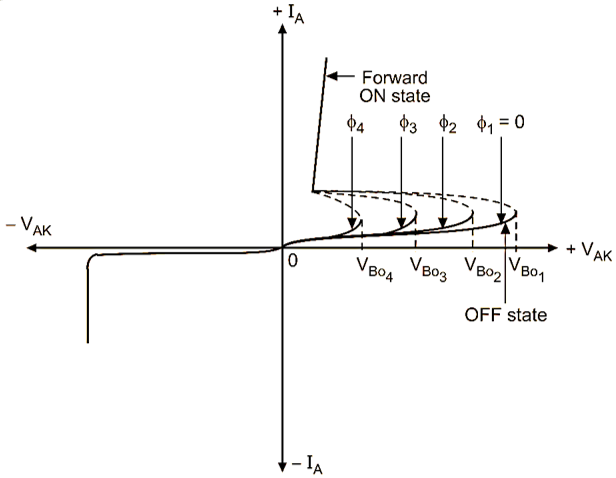
Fig. 3: V-l characteristics of LASCR
In the absence of light (Φ1 = 0), the LASCR is not conducting. It is shown by fonvard blocking (OFF) state. If the light of various intensity (flux) is incident, the LASCR starts conducting at lower and lower breakover voltages. It is shown by forward conduction (ON) state. After turn ON, a small voltage is established across the LASCR as SCR. It is possible to bring down the turn-ON voltage by applying a positive pulse at the gate G. It is also observed that larger the luminous flux (Φ4 > Φ3 > Φ2 > Φ1) incident on the LASCR, the lower forward voltage would need to turn-ON the LASCR.
Advantages of Light Activated SCR
The advantages of LASCR are as given below :
- It is small in size and light in weight.
- It dissipates low power in the ON state.
- It is free from sparking.
- It has a low turn-ON time.
Applications of Light Activated SCR
The applications of LASCR are as given below :
- It can be used as a photoelectric relay.
- It can be used to trigger high power SCR.