In this topic, you study Methods of Earthing – Theory & Diagram.
Any metal plate, pipe, rod, other conductor embedded in earth and which makes an effective electrical connection with the general mass of earth is known as earth electrode. For small installations such as residential buildings, one electrode is sufficient, in addition to the earth connection through the overhead or underground service connection. For larger installations including substations, several electrodes connected together in parallel are to be provided.
Earthing through a Water Main
In city areas, an underground water main system having metal to metal joints is sometimes used for earthing purposes. While making the earthing connection to the main water pipe, a specially designed earthing clamp is normally used to limit the contact resistance to the minimum. This method is, however, not useful if water mains are of concrete or cement.
Plate Earthing
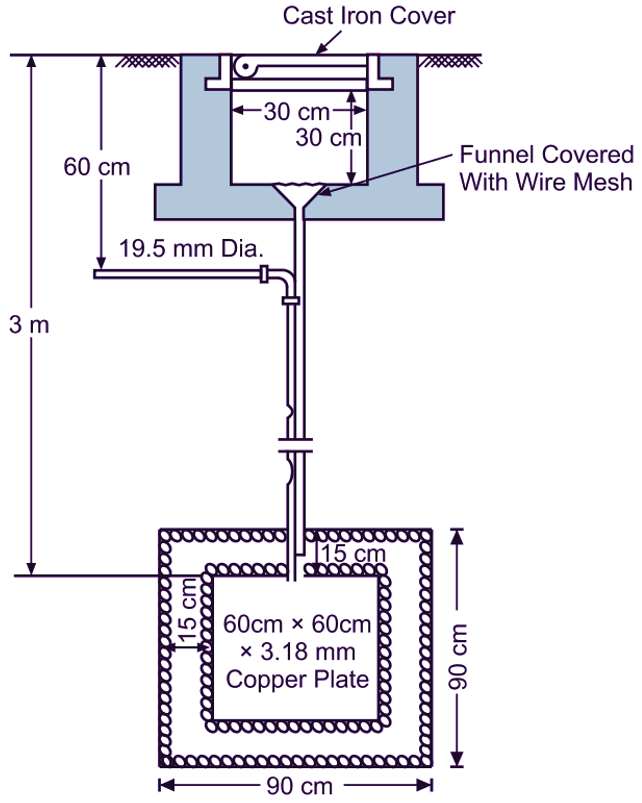
In this method as illustrated in Fig. 1, the earth wire is securely bolted to the earth plate either of copper (minimum size : 60 cm × 60 cm × 3.18 mm) or of galvanized iron (minimum size : 60 cm × 60 cm × 6.35 mm) burried in the ground to the depth of 3 m.
The plate is kept in vertical position and is embedded in an alternate layer of coke and salt, each with a minimum thickness of about 15 cm. The layers of coke and salt help to reduce the earth resistance. A galvanized iron pipe fitted with funnel at the top is provided to pour salty water in the pit of earth plate from time to time in the summer season when the moisture content in the soil reduces to a large extent.
(a)
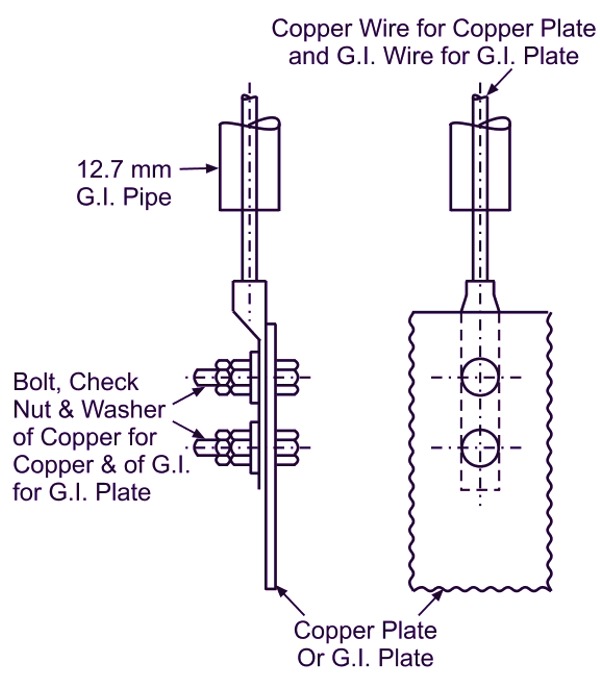
(b)
Fig. 1: Plate Earthing
Pipe Earthing
In this method (Fig. 2), the galvanized iron pipe of not less than 38.1 mm diameter and 2 m in length for ordinary soil and 2.75 m for dry and rocky soil is embedded vertically in the ground to work as earth electrode. The depth at which the pipe should be burried in the ground depends upon the soil condition. The earth wire is fastened to the top section of the pipe with nut bolts. The pit area around the galvanized iron pipe is filled with alternate layers of salt and broken pieces of coke or charcoal. A funnel is fitted to the galvanized iron pipe at the top to pour salty water in the pit of earth electrode from time to time in the summer season as mentioned in the case of plate earthing.
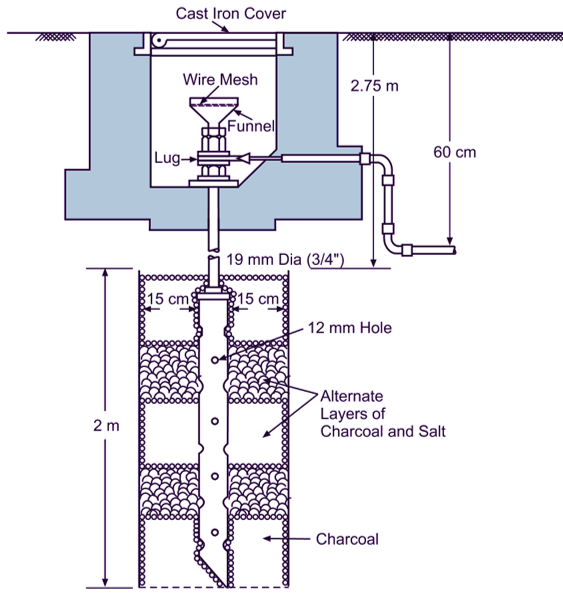
Fig. 2: Pipe earthing
In this method, the earth wire connection with galvanized iron pipe being above the ground level, it can be easily checked for carrying out continuity tests as and when desired. It is an advantage of this method over the plate earthing.