In this topic, you study the definition, working, construction, applications & diagram of the Potentiometer.
It is an instrument used for measuring the unknown e.m.f., or potential difference by balancing it wholly or partially by a source of current in the network of known characteristics. The e.m.f.s are measured directly with the potentiometer in terms of the e.m.f. of a standard cell. The current, voltage and power can be measured by means of the potentiometer and if time is known or given then the electrical energy also.
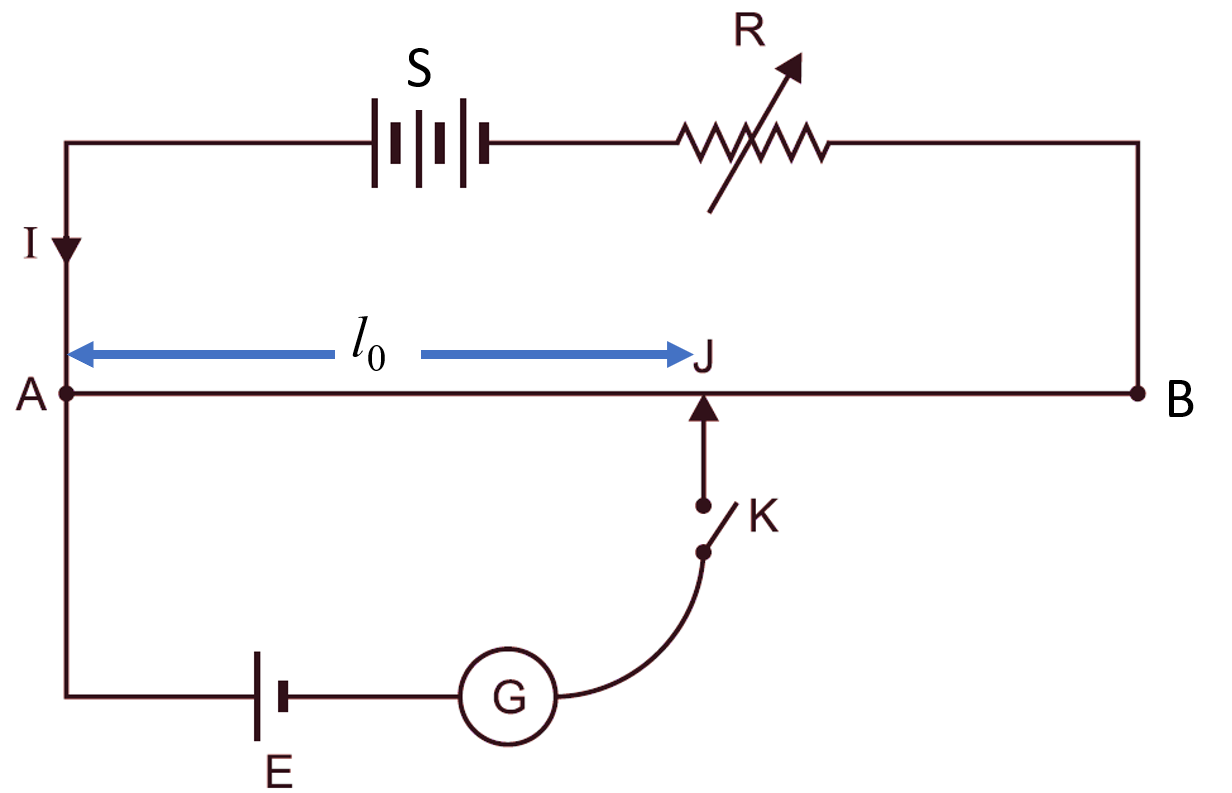
Fig.1: Potentiometer.
Working principle of Potentiometer
Whenever the negative of source is connected to negative of other source and positive with positive, the e.m.f. are opposed, and there will not be any circulating current if the potential differences are same.
Construction of Potentiometer
The diagram Fig 1 shows the construction of a simple potentiometer. It consists of a German silver or manganin wire, which has uniform cross-section and stretched between two terminals A and B. A mm scale is also attached near the wire usually of one metre in length. The ends A and B are connected to a battery through an external resistance R. The cell which is to be tested is also connected. The galvanometer indicates the balancing stage. The key is also used to make and break the contact.
Working of Potentiometer
Let a cell E be connected with its positive connected to A and negative to B through a galvanometer and a key (K) closed. Since the wire AB is of uniform cross-section so the voltage drop per mm will be constant thus by using and moving the sliding contact on the wire a point can be located where there will not be any current in galvanometer. This point will have the same potential as that of the cell under measurement.
For giving the correct reading first of all the potentiometer is standardised. A standard cell is used for that purpose whose e.m.f. is a Constant one 1 .0183 volt. The sliding contact is set so that there is deflection of the galvanometer. Let the distance l0, and voltage of the cell v0. Then
l0 v0 = 1.0183
Thus after standardisation, the specimen is used but the resistance R should no case be disturbed. Now the reading obtained from the scale will give the required value in terms of length. For more precise readings the length of wire may be increased.
Applications and Use of Potentiometer
- It is used for the measurement of e.m.f.s up to 2 V and can be used up to 250 V.
- It is used for comparing the e.m.f.s.
- It is used for measuring unknown resistance.
- It can be used for measuring current and for calibration of ammeter also.
- It is used for calibrating voltmeter.
- It is used for wattmeter calibrations.