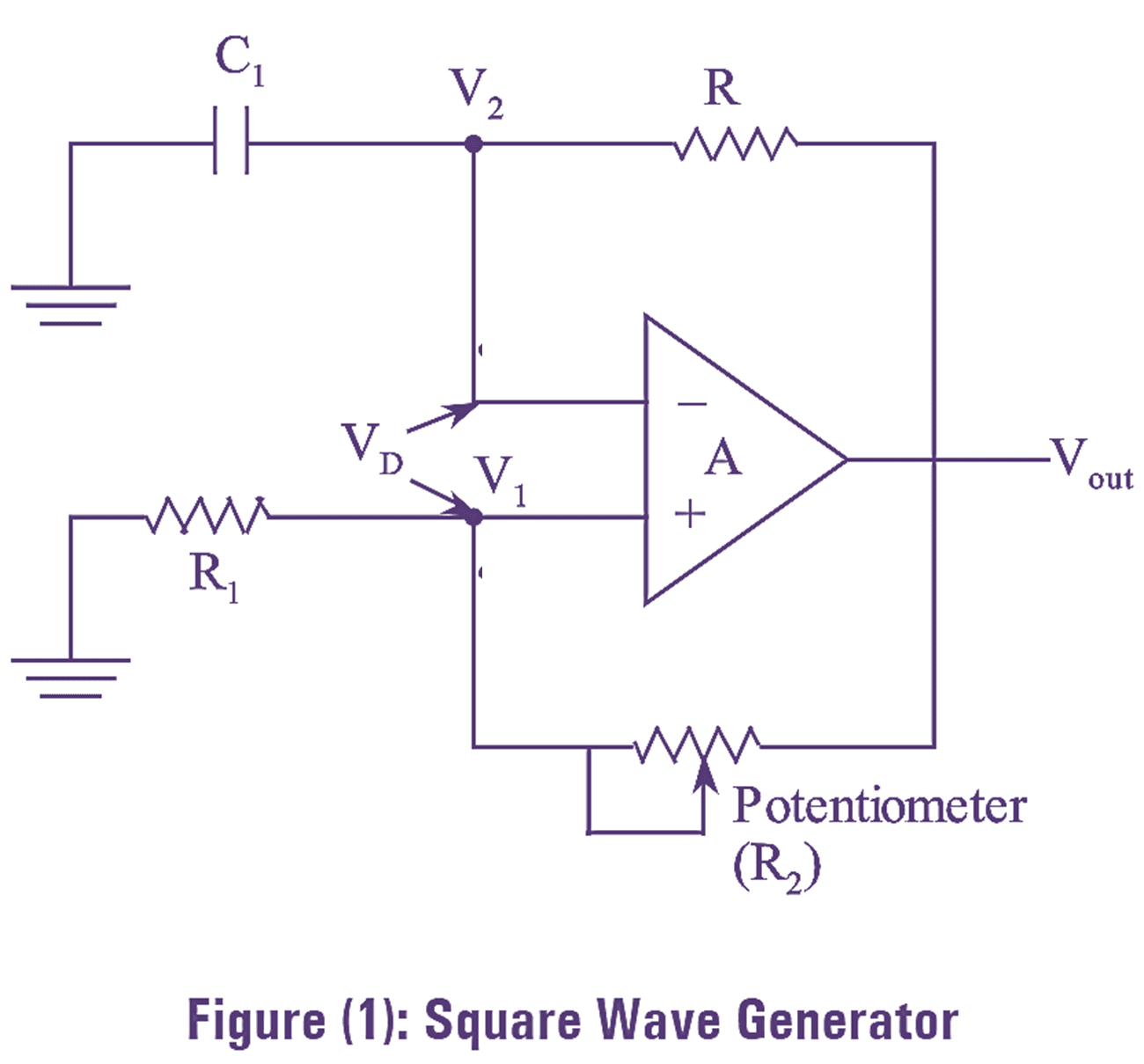
The circuit arrangement of square wave generator is as shown in figure (1). A square wave is generated when the output of op-amp swings between +Vsat and -Vsat. The output of the op-amp depends on the differential voltage VD. If the differential voltage is negative, the op-amp output is in positive saturation. If VD is positive, the op-amp output is in negative saturation.
When the supply voltages are applied, the voltage across the capacitor is zero. So, the inverting terminal voltage is zero initially It means that the voltage at V2 is zero, and the non-inverting voltage is very small and is a function of output offset voltage. So, the differential voltage,
\[{{V}_{D}}={{V}_{1}}-{{V}_{2}}\]
Since, V2 = 0
\[{{V}_{D}}={{V}_{1}}\]
In the square wave generator, the op-amp is driven into the saturation region by the non-inverting voltage, V1. If V1 is positive, C1 acts as a short circuit and starts disconnecting rapidly. Since, the op-amp gain is very large, the output is driven to +Vsat by the non-inverting terminal voltage. The resistor R drives the capacitor C1 to start charging towards +Vsat then, the voltage V1 is slightly more positive than V2 the output is forced to switch to -Vsat Then, the voltage across non-inverting terminal is expressed as,
\[{{V}_{1}}=\frac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}(-{{V}_{sat}})\]
Therefore, the differential voltage (VD = V1 – V2) is negative and holds till C1 discharges the output at negative saturation. At negative voltage, the capacitor starts charging with voltage higher than -V1. The positive VD drives the op-amp output back to +Vsat. Hence, the non-inverting input voltage is given by,
\[{{V}_{1}}=\frac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}(+{{V}_{sat}})\]
\[T=2R{{C}_{1}}ln\left( \frac{2{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)\]
Where,
T = Output waveform time period
Output frequency f0 is given by,
\[{{f}_{0}}=\frac{1}{T}Hz\]
\[=\frac{1}{2R{{C}_{1}}ln\left[ (2{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}})/{{R}_{2}} \right]}\]
If R2 = 1.16 R1, then,
\[{{f}_{0}}=\frac{1}{2\pi R{{C}_{1}}}\text{ Hz}\]
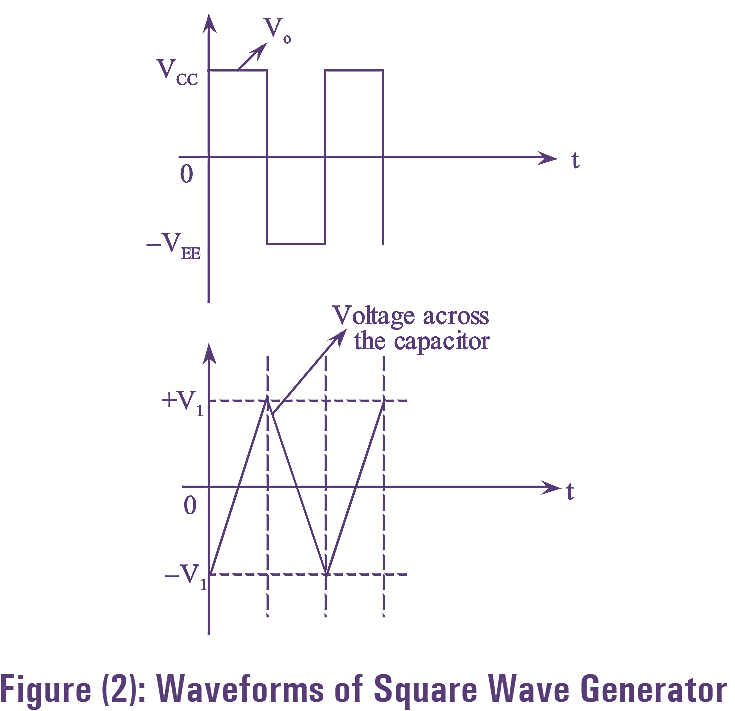
The waveforms of square wave generator are shown in figure (2).