The DIAC is an abbreviation for Diode AC semiconductor switch. The prefix ‘Di’ indicates, that the device has two terminals like diode. ‘AC’ means that the device controls the alternating current (a.c.) or can conduct current in either direction. In the thyristor family, the DIAC is used most commonly as a triggering device to trigger the TRIACs. Continue reading What is DIAC? Working, Symbol, Construction, Characteristics & Applications
Category: Power Electronics
Class D Commutation of Thyristor | Impulse commutation | Auxiliary Voltage Commutation
The auxiliary voltage commutation is also called as “Impulse commutation”, or class D commutation. The circuit diagram for class D type commutation is as shown in Fig. 1(a). SCR1 is the main load carrying SCR whereas SCR2 is an auxiliary SCR which is turned on to turn off the main SCR. Auxiliary SCR is a low-power device. The auxiliary SCR, i.e. SCR2 is turned on first in order to charge the commutating capacitor C with the polarities as shown in Fig. 1(b). As soon as C is charged, SCR2 will turn off due to a lack of current. Thus SCR2 gets commutated naturally. This positive voltage will then be held on the commutating capacitor, as there is no discharge path for it. Continue reading Class D Commutation of Thyristor | Impulse commutation | Auxiliary Voltage Commutation
Class A Commutation of Thyristor (SCR) | Current Commutation of Thyristor (SCR)
Load in Parallel with the SCR
The class A commutation is also called as self commutation. Fig. 1 shows the SCR circuit that uses a class A commutation. Continue reading Class A Commutation of Thyristor (SCR) | Current Commutation of Thyristor (SCR)
What is Semiconductor Fuse? Working, Diagram & Selection
Semiconductor Fuse is a power device required to be protected against large currents. The semiconductor fuse is the fast-acting fuse that is normally used to protect the semiconductor devices. The physical appearance of a semiconductor fuse is as shown in Fig. 1.
![]()
Fig. 1: Semiconductor fuse.
As the fault current increases, the fuse connected in series with the device is open circuited to protect the device. The nature of fuse current is shown in Fig. 2. Continue reading What is Semiconductor Fuse? Working, Diagram & Selection
What is Current Source Inverter? Working, Diagram & Waveforms
Before we go into the circuit details of CSI we must know the difference between a VSI and a CSI. The voltage and current sources are as shown in Figs .1(a) and (b) respectively.
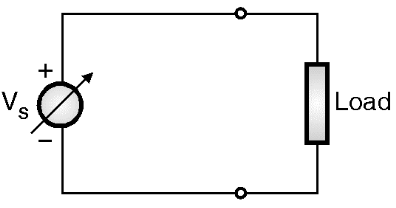
(a) Voltage source
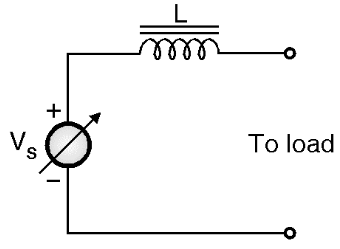
(b) Current source
Fig.1: Different types of sources.
The current source is derived from the voltage source by connecting a large value inductance in series with the voltage source as shown in Fig. 1(b). The important points to be remembered about a current source are: Continue reading What is Current Source Inverter? Working, Diagram & Waveforms
Difference Between Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) and Current Source Inverter (CSI)
In this topic, you study the Difference Between Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) and Current Source Inverter (CSI).
Continue reading Difference Between Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) and Current Source Inverter (CSI)
What is Snubber Circuit? Working, Diagram & Need
The transient overvoltages can switch on the thyristor. In some cases, the thyristor can be damaged due to these transient voltages. These transient voltages are very common when the converter is having inductive loads. The thyristors T1 can be protected against transient voltages by a RC network as shown in Fig. l. This RC network is connected in parallel across the thyristor T1. It is called snubber circuit.
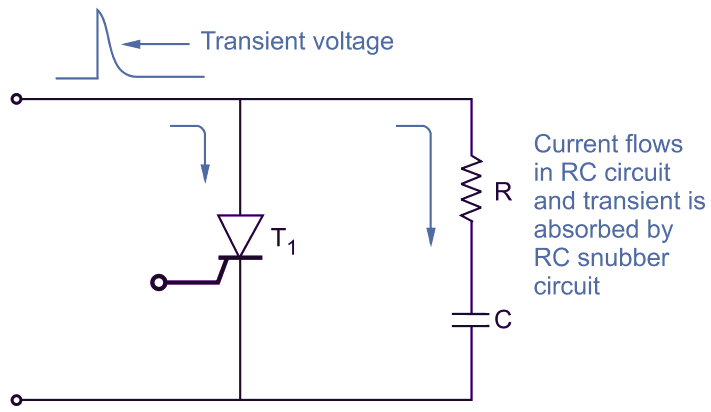
Fig. 1: A snubber (RC) network is used for transient voltage protection.
Every thyristor has maximum permissible value of $di/dt$. The thyristor can di be protected from excessive $di/dt$ by using an inductor in series as shown in Fig. 2. The inductance opposes for rapid current variations $di/dt$. Whenever there is rapid current variation, the inductor smooths it and protects the thyristor from damage.
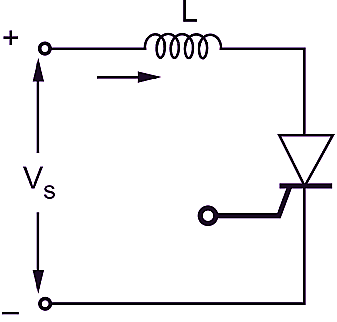
Fig. 2: An inductance in series with the thyristor provides protection against $di/dt$.
Following equations are used to calculate the values of snubber components.
\[C={{\left( \frac{0.564{{V}_{m}}}{dv/dt} \right)}^{2}}\]
\[R=2\sigma \sqrt{\frac{L}{C}}\]
\[L\ge \frac{{{V}_{S}}}{di/dt}\]
What is Online UPS? Working, Block Diagram & Applications
The online UPS is also called inverter preferred UPS.
Block Diagram & Working of Online UPS
Fig. 1 shows the block diagram of online UPS.
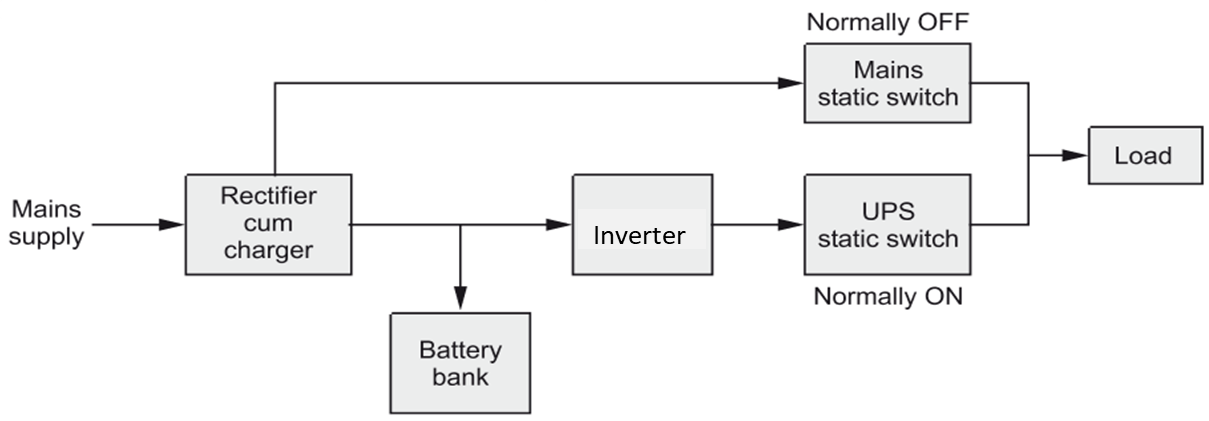
Fig. 1: Block diagram of the online UPS system. Continue reading What is Online UPS? Working, Block Diagram & Applications
What is Offline UPS? Working, Block Diagram & Applications
The offline UPS is also called line preferred UPS.
Block Diagram of Offline UPS
Fig. 1 shows the block diagram of an offline UPS. When mains supply is present, the charger charges the battery. The inverter is off and UPS static switch is off. The load is connected to mains through mains static switch.
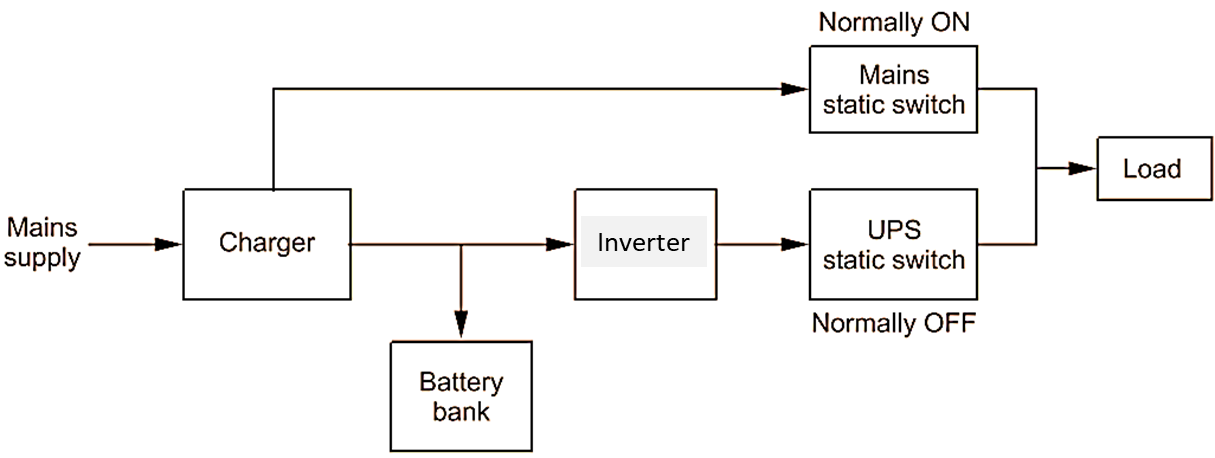
Fig. 1: Block diagram of offline UPS. Continue reading What is Offline UPS? Working, Block Diagram & Applications